- Fullstack Insider
- Posts
- How to Solve the Two Sum Problem (Step-by-Step Guide with Examples)
How to Solve the Two Sum Problem (Step-by-Step Guide with Examples)
It looks simple, but the way you solve Two Sum shows whether you think like a beginner or an engineer.

👋 Hello, Harman here Welcome to this week’s Fullstack Insider newsletter.
📢 How to Solve the Two Sum Problem (LeetCode #1) in Python — Brute Force and Optimized Solutions
If you’re preparing for coding interviews, this guide will walk you through solving the Two Sum problem step by step, with detailed explanations, code, and examples.
Hey Builders 👋,
The Two Sum problem is one of the most famous coding interview questions. It’s literally LeetCode Problem #1, which makes it the “hello world” of interview prep.
At first glance, it looks straightforward: “Find two numbers in an array that add up to a target.”
But here’s the thing—how you solve it matters more than just solving it.
A brute force solution will work, but it shows you’re thinking like a beginner.
An optimized solution, on the other hand, demonstrates that you know how to use data structures efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll cover both approaches step by step, with detailed code, dry runs, and explanations.
🚀 Why This Matters
Interview Favorite → It’s one of the most common warm-up problems in interviews at FAANG, startups, and big tech companies. If you can’t solve Two Sum, you’ll struggle with harder problems.
Teaches Core Concepts → You’ll practice working with arrays, hash maps (dictionaries in Python), and learn about time complexity (
O(n²)vsO(n)).Real-World Use Cases → Believe it or not, this concept comes up in real software:
Budget apps (finding two expenses that match a limit).
E-commerce (two items that add up to a gift card balance).
Payment systems (matching transactions that equal a given amount).
🛠 Problem Statement
Here’s the official problem statement from LeetCode:
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return the indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example

Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9.
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1] 🔑 Step 1: Brute Force Solution
When you first see this problem, the obvious way is:
Take each number in the list.
Pair it with every other number.
Check if their sum equals the target.
This is called the brute force approach.
Code:
def twoSum(nums, target):
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]Walkthrough:
For nums = [2, 7, 11, 15] and target = 9
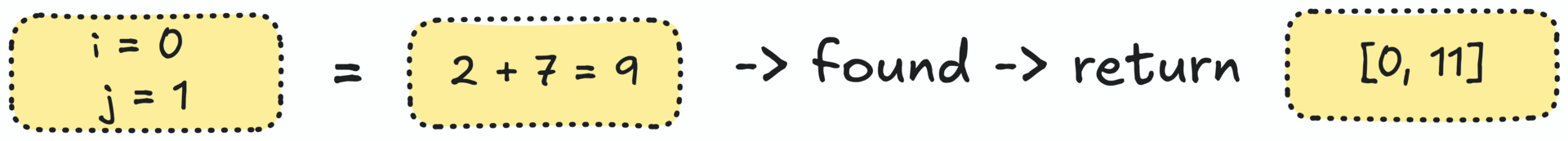
Time & Space Complexity:
Time Complexity: O(n²) → for every number, you check every other number.
Space Complexity: O(1) → no extra memory used.
✅ Easy to understand.
❌ Very slow when nums is large (e.g., 10⁵ numbers).
🔑 Step 2: Optimized Solution Using Hash Map
The brute force works, but let’s think like an engineer:
Can we avoid checking every pair?
Yes. We can use a hash map (dictionary in Python) to store numbers we’ve already seen.
The idea:
For each number, calculate its “complement” →
complement = target - num.Check if this complement is already in the hash map.
If yes → we found the answer.
If no → store the current number in the hash map and continue.
Code:
def twoSum(nums, target):
hashmap = {}
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
complement = target - num
if complement in hashmap:
return [hashmap[complement], i]
hashmap[num] = iWalkthrough:

i = 0 → num = 2 → complement = 7 → not in hashmap → store
{2:0}.i = 1 → num = 7 → complement = 2 → 2 is in hashmap → return
[0,1].
Done ✅
Time & Space Complexity:
Time Complexity: O(n) → only one pass through the list.
Space Complexity: O(n) → we store elements in the hash map.
✅ Much faster for large arrays.
✅ The go-to solution for coding interviews.
💼 From our Partners
Modernize your marketing with AdQuick
AdQuick unlocks the benefits of Out Of Home (OOH) advertising in a way no one else has. Approaching the problem with eyes to performance, created for marketers with the engineering excellence you’ve come to expect for the internet.
Marketers agree OOH is one of the best ways for building brand awareness, reaching new customers, and reinforcing your brand message. It’s just been difficult to scale. But with AdQuick, you can easily plan, deploy and measure campaigns just as easily as digital ads, making them a no-brainer to add to your team’s toolbox.
🔑 Step 3: Edge Cases to Consider
When coding interviews get tricky, they’ll throw in edge cases. Think about:
Negative numbers → Works fine (
[-3,4,3,90], target = 0).Duplicates → Make sure you don’t reuse the same number twice.
Large arrays → Optimized O(n) solution is necessary for performance.
🔑 Step 4: Tips for Interviews
Start with the brute force → shows you understand the problem.
Then optimize with the hash map → shows you can improve efficiency.
Talk about time complexity (O(n²) vs O(n)) → shows you know trade-offs.
Always dry run your solution with a small example → helps avoid mistakes.
✅ Pro Tip
In real-world coding interviews, interviewers don’t just care about the final code. They care about how you think.
So when asked about Two Sum:
Explain the brute force method first.
Then say, “But this is inefficient. Here’s how we can optimize with a hash map.”
Write the optimized code.
This shows both clarity of thought and technical depth.
💬 Question for You
When you face a new coding problem, what’s your first instinct?
Try brute force right away?
Or think about optimization first?
Reply and let me know—I’ll feature the best answers in the next edition.
Want to be featured?
Send us email → [email protected] to get featured
If you like today’s issue, consider subscribing to us.
That’s a wrap! Catch you in next edition. 👋
—Harman



Reply